In January, shipments of small and medium-sized display panels were approximately 171.3 million, a significant decrease of 14% from 198.6 million in December 2011. This is the largest monthly decline in the industry in the past 12 months and the fourth consecutive month since October last year.
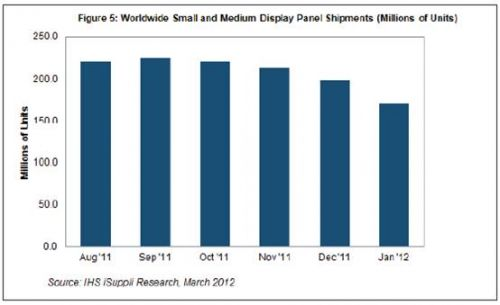
The rate of decline in January was twice that of last December. In the first quarter of each year, shipments of small and medium-sized display panels are generally low. At this time, manufacturers clean up inventory, and panel factories are preparing to increase production in the second quarter. Small and medium-sized display panels refer to panels smaller than 10 inches in size.
The capacity utilization rate of Taiwanese manufacturers decreased from 62% in the previous quarter to 58%, leading to a drop in the shipment of small and medium-sized display panels to 131.3 million in January, a decrease of 29 million from December 2011. Taiwan's six suppliers are ranked in descending order of shipment volume: Chunghwa Picture Tubes, Chi Mei Optoelectronics, HannStar Display, Shenghua Technology, AUO and Lingju Technology.
On the other hand, the capacity utilization rate of South Korean manufacturers maintained at the level of last December, and the shipment volume in January increased by 4.4% to 40 million. IHS Company believes that the shipments of Samsung Display and LG Display will increase due to the increase in the production capacity of AMOLED panels. Samsung's two 5.5-generation factories have started mass production.
Taiwanese and Korean manufacturers have dominated the small and medium-sized display panels, and newcomers from mainland China are also constantly strengthening their capabilities. White-brand mobile phone manufacturers provide a market for low-cost displays, and Tianma Microelectronics and BOE Display Technology continue to ship a large amount to the market.
With low prices and a strategy of incorporating white-brand smartphones and tablets into the product mix, Chinese manufacturers hope to win a slice of the dominant Taiwanese manufacturer. However, whether Chinese manufacturers can achieve greater success depends not only on their ability to acquire key intellectual property rights, but also on whether Chinese suppliers can produce high-quality panels. These intellectual property rights involve technologies such as IPS/AFFS, AMOLED, and 3D.
In this regard, South Korean manufacturers may have a competitive advantage, they are actively developing the eighth generation of factories, and focus on capital expenditure to increase AMOLED production capacity above. Samsung Electronics spun off the display business and set up a new Samsung monitor. Samsung Mobile Display, which focuses on OLED production, may become part of Samsung Display in the future, helping to strengthen Samsung’s position in the small and medium-sized display market, especially in the AMOLED field. Taiwanese manufacturers want to launch their own AMOLED panels to compete with South Korean counterparts, but in 2012 they could only account for a small share of the total small and medium-sized display market shipments, hindering their influence on the industry.
In January, the average selling price of small and medium-sized display panels for mobile phone displays increased, but the prices of digital cameras and tablet PCs fell. The increase in the average sales price of mobile phone panels stems from the adoption of new high-profile displays in the high-end and low-end smartphone markets. At the same time, despite the relatively large shipments, the decline in the price of digital camera panels is mainly due to the impact of high-end smartphones with high-resolution cameras. Tablet PC panel prices were lower in January because channel inventory impacted the demand for monitors, and it coincided with the low season.
In March, Apple introduced the new iPad tablet that the market is looking forward to, with 9. The x-inch QXGA display has a resolution of 2048 x 1536 pixels (264 pixels per inch) and is twice that of the iPad 2. For display suppliers, it is very challenging to achieve such a high specification without sacrificing power efficiency, image brightness, and color.
The possible suppliers for the new iPad display are Samsung, LG Display and Japan Sharp. However, it is believed that the new iPad's display screen presents challenges to LG Display and Sharp's panel yield and quality, which may lead to longer lead times and affect the availability of new iPad displays.
The author Vinita Jakhanwal is senior director of small and medium displays at IHS.
The off-grid inverter is an inverter used in off-grid solar power generation systems. Its main function is to convert the direct current generated by solar panels into alternating current to meet the power demand in off-grid environments, such as in remote areas, In camping, boats, or moving vehicles.
Main effect:
Converts the direct current generated by solar panels into alternating current to supply the power needs of homes, mobile devices, or other electrical appliances.
Off-grid inverters are usually equipped with battery energy storage systems, which store excess power so that they can continue to supply power when the solar panels cannot generate enough power.
Differences from On-Grid Inverter:
Connection method: Off-grid inverter is an inverter used in the off-grid system and does not need to be connected to the grid. They are often used in places where there is no access to the grid, such as remote areas, wild camping, or outlying islands.
Grid requirements: Unlike on-grid inverters, off-grid inverters do not need to meet grid requirements and standards because they are not connected to the grid. They can operate independently and can be adapted to different off-grid environments.
Self-sufficiency: The off-grid inverter is equipped with a battery energy storage system, which can store excess electricity so that it can continue to supply electricity when the solar panels are unable to generate electricity. This makes the off-grid system self-sufficient and not dependent on an external grid for power.
Application scenarios: Off-grid inverters are widely used in remote areas, camping, ships, mobile vehicles, and some special-purpose scenarios. On the other hand, grid-connected inverters are mainly used in home, commercial, and industrial photovoltaic power generation systems connected to the grid.
In general, the main function of the off-grid inverter is to convert the direct current generated by the solar panels into alternating current to meet the power demand in the off-grid environment and achieve self-sufficiency by being equipped with a battery energy storage system. In contrast, on-grid inverters connected to the grid are mainly used to integrate solar power into the grid, realize the interaction between solar power and the grid, and comply with the requirements and standards of the grid.
off grid solar inverter,off grid 3 phase inverter, off grid solar power inverter, off grid solar inverter 5kw, off grid solar inverters for sale
Ningbo Autrends International Trade Co., Ltd. , https://www.aitsolarpanels.com