High temperatures can cause the probability of failure of electronic components to increase rapidly, resulting in a decrease in the reliability of LED displays . In order to control the temperature of the electronic components inside the LED display so that it does not exceed the specified maximum allowable temperature under the working environment under which the LED display is placed, the heat dissipation design of the LED display is required. The heat dissipation design of the LED display, how to achieve low cost and high quality, is the content of this article. 
First, the knowledge of heat dissipation design
The two basic laws of heat transfer: heat flows from the high temperature zone to the low temperature zone; the heat generated by the high temperature zone is equal to the heat absorbed by the low temperature zone.
There are three basic ways of transferring heat: heat conduction, convection, and radiation.
Thermal conduction: Gas heat conduction is the result of collisions between gas molecules when they move irregularly. The heat conduction in the metal conductor is mainly achieved by the movement of free electrons. Thermal conduction in non-conductive solids is achieved by vibration of the lattice structure. The heat conduction mechanism in the liquid mainly depends on the action of elastic waves.
Convection: refers to the heat transfer process caused by the relative displacement between various parts of the fluid. Convection only occurs in the fluid and is necessarily accompanied by thermal conduction. The heat exchange process that occurs when fluid flows over the surface of an object is called convective heat transfer. The convection caused by the difference in density of the various parts of the fluid is called natural convection. If the motion of the fluid is caused by an external force (fan, etc.), it is called forced convection.
Radiation: The process by which an object transmits its ability in the form of electromagnetic waves is called thermal radiation. Radiant energy transfers energy in a vacuum and has a conversion in the form of energy, that is, thermal energy is converted into radiant energy and radiant energy is converted into thermal energy.
When selecting the heat dissipation method, the following factors should be considered: heat flux density, volume power density, total power consumption, surface area, volume, and working environment conditions (temperature, humidity, air pressure, dust, etc.) of the LED display.
According to the heat transfer mechanism, there are natural cooling, forced air cooling, direct liquid cooling, evaporative cooling, thermoelectric cooling, heat pipe heat transfer and other heat dissipation methods.
A comparison of several common cooling methods is as follows:
It can be seen from the above table that the heat dissipation effect of natural cooling is relatively small, and the heat dissipation effect of evaporative cooling is relatively large. The human body sweats and cools down, using the heat dissipation method of evaporative cooling.
Second, the LED display heat dissipation design method
As can be seen from practical applications, the current LED display has more internal heat, and the electronic components with more heat are: LED, driver IC, and switching power supply. Therefore, it is necessary to heat-dissipate the LED display to provide a low thermal resistance path between the heat source and the external environment to ensure the smooth transfer of heat.
When the temperature of the object is lower than 1800 °C, the meaningful thermal radiation wavelength is between 0.38 and 100 μm, and most of the energy is in the range of 0.76~20μm in the infrared band. In the visible light band, the specific gravity of the thermal radiation energy is not large. Therefore, the interior of the LED display can be freely coated with various colors. The outside of the LED display that is exposed to direct sunlight should be painted in a light color to avoid absorption of visible light.
Considering the use of the LED display screen, the rental screen and the indoor fixed installation screen mostly use the method of natural cooling and heat dissipation, and the outdoor fixed installation screen uses the method of forced air cooling to dissipate heat.
The LED display is fixedly installed outdoors, and the heat dissipation design should be considered when installing the entire screen. Due to the limitation of the installation location, as the power consumption of the LED display is reduced, more and more customers are naked in the LED display, and there is no other auxiliary cooling measures. For the large screen of the LED display, only the way of natural cooling and heat dissipation is relatively poor. Therefore, the heat dissipation design of the LED display box is particularly important. Considering the reliability and maintenance cost of the LED display box, it is a better way to dissipate heat by using a fan for forced convection cooling.
The heat exchange area between the heating electronic components and the cold air, the temperature difference between the heating electronic components and the cold air directly affects the heat dissipation effect. This involves the design of the air volume entering the LED display cabinet and the design of the air duct. When designing the ventilation duct, try to use straight pipeline to transport air to avoid the use of sharply bent and curved pipelines. Ventilation ducts should avoid sudden expansion or sudden contraction. The extended opening angle should not exceed 20o, and the shrinking cone angle should not exceed 60o. Ventilation ducts should be sealed as much as possible, and all overlaps should follow the direction of flow.
There are several points to note when designing the LED display box: the air inlet should be placed on the underside of the cabinet, but not too low to prevent dirt and water from entering the cabinet installed on the ground. The venting holes should be placed close to the upper side of the cabinet. Air should circulate from the bottom of the box, and a dedicated air inlet or vent should be used. Cooling air should flow through the hot electronic components while preventing short-circuiting of the airflow. A filter screen should be provided at the air inlet and outlet to prevent debris from entering the cabinet. Design should be such that natural convection helps to force convection. Be sure to keep the air intake and exhaust away from the design. Avoid reusing cooling air. Considering the factor of air volume expansion, the air outlet area should be 1.5 times to 2 times the area of ​​the air inlet. Electronic components with large heat generation such as switching power supplies should be placed as close as possible to the air inlet. To ensure that the direction of the heat sink cogging is parallel to the wind direction, the heat sink slot cannot block the air path.
The fan is installed in the system. Due to structural constraints, the air inlet and outlet are often blocked and the performance curve changes. According to practical experience, the inlet and outlet of the fan should preferably be 40mm away from the barrier. If there is space limitation, it should be at least 20mm.
The selection of the fan is generally based on the size of the fan inlet and outlet air temperature. In the case of ventilation, since the fan draws hot air, it will have a serious impact on the life of the fan. For fan manufacturers, 60 °C is generally used as the condition for calibrating the fan life MTBF. If the ambient temperature of the fan application is higher than 60 °C, the fan life is reduced by half for every 5 °C increase in temperature.
When considering the use of ventilation or air blowing, you can refer to the following table for comparison of air blowing and ventilation.

The heat dissipation design of the module inside the box is also considered. Poor heat dissipation design will result in poor display performance and color spots. When placing the heating components on the PCB, consider the uniform distribution of heat as much as possible, and do not concentrate the components with more heat on a part of the PCB.
The figure below shows the flow chart of the heat dissipation design.
Fiber Optical Splice Closure(FOSC) is provided to provide a solid protection for fiber optic splice points, YULIANG Telecom offers a full range, various models of FOSC with both Inland type and DOME types, YULIANG Telcom FOSC are applied for underground, aerial, pipeline, manhole with protection level reaches IP68.
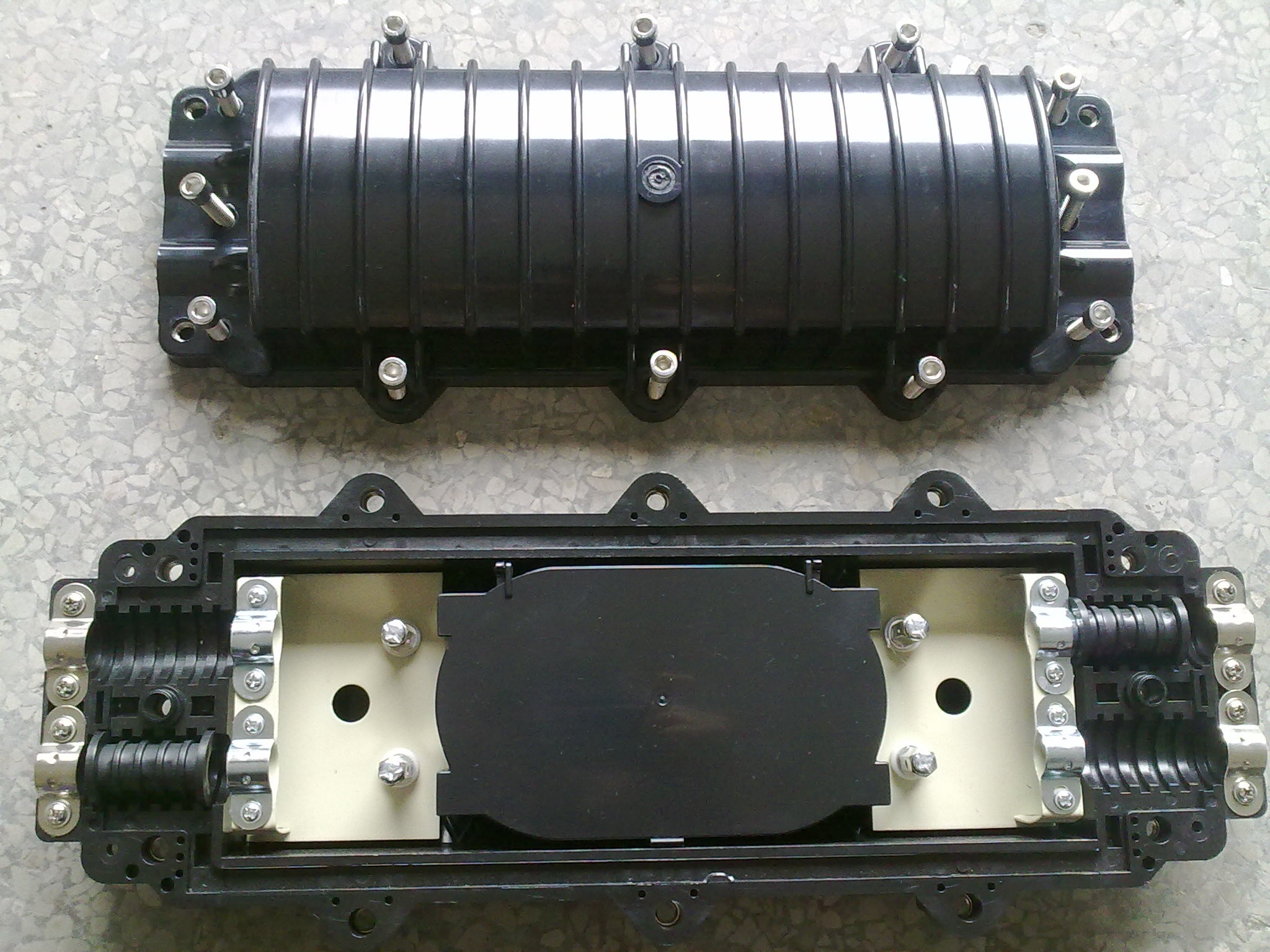
Fiber Optic Splice Closure,Fiber Splice Enclosure,Optical Fiber Splice Closure,Fiber Optical Splice Closure
NINGBO YULIANG TELECOM MUNICATIONS EQUIPMENT CO.,LTD. , https://www.yltelecom.com