NB-IoT is the current hot spot in the telecom industry. Investors in the secondary market are more concerned. Everyone has a lot of questions about what NB-IoT is and what it can do. Next, explain the relationship between NB-IoT and the Internet of Things. Welcome everyone. Related issues are discussed with us.
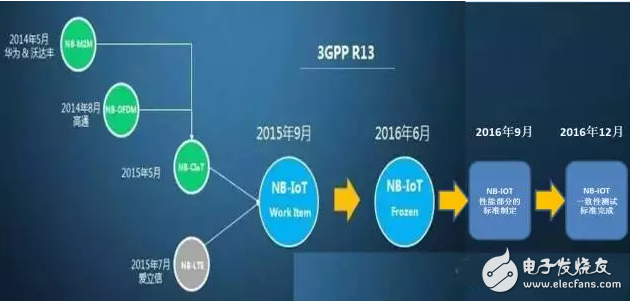
On June 16, 2016, the 72nd meeting of the 3GPP RAN Plenary held in Busan, South Korea, was successfully concluded. NB-IoT (Narrow Band Internet of Things) is an important topic of 3GPP R13, and its corresponding 3GPP protocol-related content has been approved by the RAN Plenary, officially proclaiming the NB-IoT standard widely supported by the wireless industry. After more than two years of research on the core protocol, it has finally been completed.

From the start of the work in September 2015 to the freezing of the standards in June 2016, the rapid progress reflects the urgent need. According to the plan, the core part of NB-IoT's 3GPP standard will be frozen in June 2016, and the performance part of the standard will be completed in September 2016. The final conformance test standard will also be completed in December 2016. The global operator has a proprietary IoT-based protocol, and the successful completion of the standardization work also marks the upcoming commercial phase of NB-IoT. NB-IOT will have a lot of application space in the window before 5G commercial and the low-cost and low-rate market after 5G commercial. Some chip and module manufacturers have planned to support NB-IOT this year.
1. What is NB-IoT?
NB-IoT, the Narrow Band-Internet of Things, is a kind of Internet of Things technology with low cost, low power consumption and wide coverage. It is positioned at carrier-grade, low-rate based on licensed spectrum. The networking market has broad application prospects. The six major application scenarios of NB-IoT technology are precisely the difficult scenarios supported by existing mobile communications, including location tracking, environmental monitoring, smart parking, remote meter reading, agriculture and animal husbandry. Market research firm Machina predicts that NB-IoT will cover 25% of IoT connections in the future.
NB-IoT is an important enhancement to 3GPP R13 Phase LTE with RF bandwidth as low as 0.18MHz. NB-IoT is a fusion of NB-CIoT and NB-LTE standards, balancing the interests of all parties and adapting to a wider deployment scenario. Among them, Huawei, Vodafone, Qualcomm and other companies support NB-CIoT; Ericsson, ZTE, Samsung, Intel, MTK and other companies support NB-LTE. Compared with the standard NB-IoT, NB-CIoT and NB-LTE have large differences, and the terminal cannot be upgraded smoothly. Some non-standard base stations even face the risk of network retreat.
2, NB-IoT's four advantages
(1) Wide coverage, NB-IoT coverage is 20 DB better than traditional GSM network. According to the coverage area calculation, one base station can provide 10 times area coverage; (2) massive connection, below 200KHz frequency, one base station can provide 100,000 connections by NB-IoT; (3) low power consumption, NB-IoT communication The module battery can work independently for ten years without charging; (4) Low cost, the target of the NB-IoT module is less than 5 dollars. The NB-IoT is based on the cellular network and can be deployed directly on the existing GSM network, UMTS network or LTE network. The carrier has lower deployment cost and will smoothly upgrade to 4.5G.
3, the sectarian battle: NB-IoT and LoRa
IoT communication technology can be divided into two categories according to the transmission distance:
(1) Short-range communication technology, representing technologies such as Zigbee, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Z-wave, etc. Typical application scenarios such as smart home;
(2) WAN communication technology, the industry is generally defined as LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network), typical application scenarios such as smart meter reading. LPWAN technology can be divided into two categories: (1) technologies that operate in unlicensed bands, such as Lora and Sigfox, which are mostly non-standard and custom implementations; (2) technologies that operate in licensed bands, such as GSM, More mature 2G/3G cellular communication technologies such as CDMA and WCDMA, as well as LTE and its evolution technologies that are gradually deployed and supported by different category types. These technologies are basically in 3GPP (mainly GSM, WCDMA, LTE and its evolution). Standards for standards related to technology) or 3GPP2 (mainly CDMA-related standards) have been defined by international standards organizations. NB-IoT is a new narrowband cellular communication LPWAN technology.
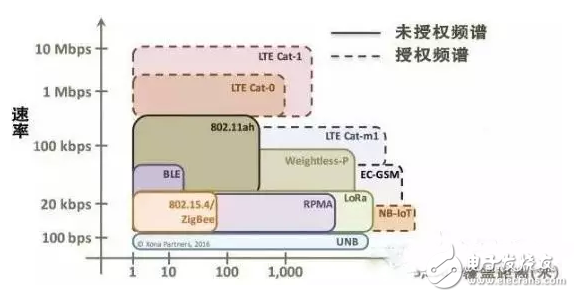
LoRa technology features: capable of long-distance transmission of 1-20km, the wireless distance in the city ranges from 1 to 2 kilometers, and the wireless distance in the suburbs can reach up to 20km. The number of nodes can be up to 10,000 or even millions, and how many nodes or terminal devices a gateway can connect to. The data rate ranges from 0.3 to 50 kbps, and the lower data rate allows battery life to reach 3-10 years.
From a technical comparison, it is difficult for NB-IoT and LoRa to see which re-technology has an absolute advantage. The biggest difference between the two is whether it works in the licensed spectrum. Due to interference problems, products based on unlicensed spectrum have only been in use for a few days, and authorized and unlicensed spectrum has become the key to the future development of NB-IoT and LoRa technologies. The addition of LoRa's enterprise-level network solution will greatly expand the market scope of the private network.
Lcd Tonch Screen For Iphone 8,Lcd Touch Screen For Iphone 8P,Lcd Display For Iphone 8P,Mobile Lcd For Iphone 8P
Shenzhen Xiangying touch photoelectric co., ltd. , https://www.starstpmobile.com