Arduino serial communication
Serial.begin();
Description
Turn on the serial port, usually in the setup() function.
grammar
Serial.begin(speed);
Serial.begin(speed,config);
parameter
Speed: baud rate, generally 300, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 14400, 19200, 28800, 38400, 57600, 115200
Config: Set the data bit, parity bit and stop bit. For example, Serial.begin(speed, Serial_8N1); Serial_8N1: 8 means 8 data bits, N means no parity, 1 means 1 stop bit.
return
None
Example
[cpp] view plain copy
Void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // opensserial port, sets data rate to 9600 bps
}
Serial.end();
Description
Disable serial port transfer function. At this time, the pin pin of the serial port transmission can be used as the digital IO pin.
grammar
Serial.end()
parameter
None
return
None
2, clear the serial cacheSerial.flush();
Description
Before the 1.0 version is to clear the serial port cache, now the function is to wait for the output data to be transferred. If you want to clear the serial port cache, you can use: while (Serial.read () 》 = 0) instead.
grammar
Serial.flush ()
parameter
None
return
None
While(Serial.read()》= 0){}
Description
The Serial.read() function reads a character in the serial port cache and deletes the read characters. So you can use this code to clear the serial port cache. The experimental code is detailed in the code below.
grammar
While(Serial.read() 》=0){}
parameter
None
return
None
3, output serial port dataThe function that prints out the serial port data is given in this section, so that you can read the various sample code that follows.
Serial.print();
Description
The serial port outputs the data function and writes the string data to the serial port.
grammar
Serial.print(val)
Serial.print(val,format)
parameter
Val: printed value, any data type
Format: The output data format, including the integer type and the number of decimal places for floating point data.
Example
Serial.print(78, BIN) get "1001110"
Serial.print(78, OCT) gets "116"
Serial.print(78, DEC) gets "78"
Serial.print(78, HEX) gets "4E"
Serial.print(1.23456, 0) gets "1"
Serial.print(1.23456, 2) gets "1.23"
Serial.print(1.23456, 4) gets "1.2346"
Serial.print('N') gets "N"
Serial.print("Hello world.") gets "Hello world."
Serial.println();
Description
Write string data and wrap it. The experimental code is detailed below.
grammar
Serial.println(val)
Serial.println(val,format)
parameter
Val: printed value, any data type
Format: The output data format, including the integer type and the number of decimal places for floating point data.
return
byte
Serial.SerialEvent();
The event function triggered when the serial port data is ready, that is, the serial port data is ready to call the function.
grammar
Serial.serialEvent{//statements}
parameter
Statements: Any valid statement.
4, read the serial buffer area dataSerial.available();
Description
Determine the status function of the serial port buffer to determine whether the data is sent to the serial port. Note that the use of delay (100) usually to ensure that the serial port characters are received, that is, to ensure that Serial.available () returns the correct number of readable bytes of the buffer.
grammar
Serial.available();
parameter
None
return
Returns the number of readable bytes in the buffer
Example
[cpp] view plain copy
Void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
While(Serial.read()》= 0){}//clear serialbuffer
}
Void loop() {
If (Serial.available() 》 0) {
Delay(100); // Wait for the data to pass
Int numdata = Serial.available();
Serial.print("Serial.available = :");
Serial.println(numdata);
}
While(Serial.read()"=0){} //Clear the serial cache
}
Experimental result
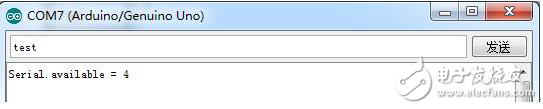
Serial.read();
Description
Read the serial port data, read one character at a time, and delete the read data after reading.
grammar
Serial.read();
parameter
None
return
Returns the first readable byte in the serial buffer, returning -1, integer type when there is no readable data.
Example
[cpp] view plain copy
Char comchar;
Void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
While(Serial.read()》= 0){}/ /clear serialbuffer
}
Void loop() {
// read data from serial port
While(Serial.available()》0){
Comchar = Serial.read();//Read the first byte of the serial port
Serial.print("Serial.read: â€);
Serial.println(comchar);
Delay(100);
}
}
Experimental result
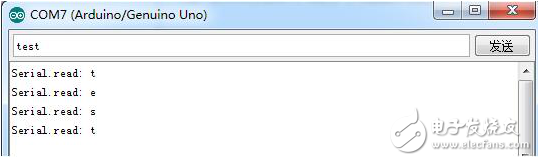
It can be seen from the experimental results that Serial.read() reads the first character from the serial port cache each time and deletes the read characters.
Serial.peek();
Description
Reads the next byte of data (character type) in the serial port cache, but does not delete the data from the internal cache. That is, consecutive calls to peek() will return the same character. Calling read() returns the next character.
grammar
Serial.peek();
parameter
None
return
Returns the data of the next byte (character) in the serial buffer. If no -1 is returned, the integer is int.
Example
[cpp] view plain copy
Char comchar;
Void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
While(Serial.read()》= 0){}//clear serialbuffer
}
Void loop() {
// read data from serial port
While(Serial.available()》0){
Comchar = Serial.peek();
Serial.print("Serial.peek: â€);
Serial.println(comchar);
Delay(100);
}
}
Experimental result
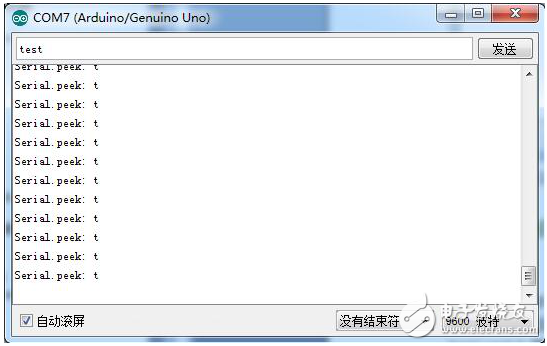
It can be seen from the experimental results that Serial.peek() does not delete the read characters every time it reads a character from the serial port cache. The same character is still the second time.
Serial.readBytes(buffer,length);
Description
Reads the character of the specified length length from the serial port to the buffer array buffer.
grammar
Serial.readBytes(buffer,length);
parameter
Buffer: cache variable
Length: set read length
return
Returns the number of characters stored in the cache, 0 means no valid data.
Example
[cpp] view plain copy
Char buffer[18];
Int numdata=0;
Void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
While(Serial.read()"= 0){}//clear serial port
}
Void loop() {
// read data from serial port
If(Serial.available()》0){
Delay(100);
Numdata = Serial.readBytes(buffer,3);
Serial.print("Serial.readBytes:");
Serial.println(buffer);
}
// clear serial buffer
While(Serial.read() 》= 0){}
For(int i=0; i“18; i++){
Buffer[i]='\0';
}
}
Experimental result
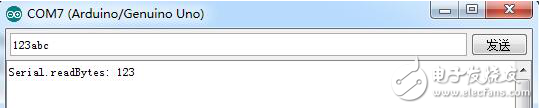
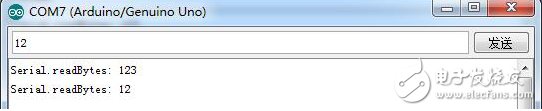
Reads a byte of the specified length of 3 from the serial port cache.
Serial.readBytesUnTIl(character,buffer,length);
Description
Reads the character of the specified length from the serial port cache to the array buffer, and stops after encountering the terminating character.
grammar
Serial.readBytesUnTIl(character ,buffer,length);
parameter
Character : the character to be found (char)
Buffer: stores a cache of read data (char[] or byte[])
Length: set read length
return
Returns the number of characters stored in the cache, 0 means no valid data.
Example
[cpp] view plain copy
Char buffer[18];
Char character = ','; //terminating characters
Int numdata=0;
Void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
While(Serial.read()》= 0){}//clear serialport
}
Void loop() {
// read data from serial port
If(Serial.available()》0){
Delay(100);
Numdata =Serial.readBytesUnTIl(character,buffer,3);
Serial.print("Serial.readBytes:");
Serial.println(buffer);
}
// clear serial buffer
While(Serial.read() 》= 0){}
For(int i=0; i“18; i++){
Buffer[i]='\0';
}
}
Experimental result
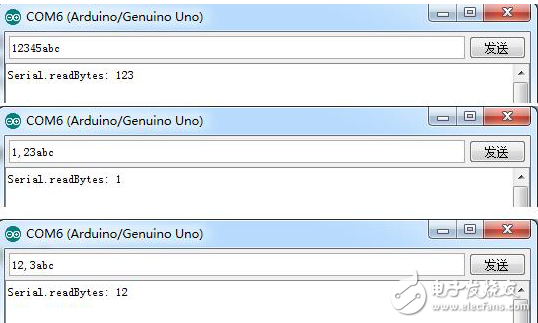
Read 3 characters from the serial port cache and terminate reading when "," is encountered.
Serial.readString();
Description
Read all data from the serial buffer to a string variable.
grammar
Serial.readString();
parameter
None
return
Returns a string read from the serial buffer.
Example
[cpp] view plain copy
String comdata = "";
Void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
While(Serial.read()》= 0){} //clear serialbuffer
}
Void loop() {
// read data from serial port
If(Serial.available()》0){
Delay(100);
Comdata = Serial.readString();
Serial.print("Serial.readString:");
Serial.println(comdata);
}
Comdata = "";
}
Experimental result
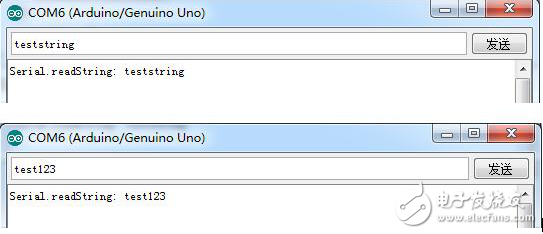
It can be seen from the experimental results that Serial.readString() reads characters from the serial cache to a string.
Serial.readStringUnTIl();
Description
Read characters from the serial buffer to a string variable until you finish reading or encounter a termination character.
grammar
Serial.readStringUntil(terminator)
parameter
Terminator: terminating character (cha type)
return
The entire string read from the serial buffer until the termination character is detected.
Example
[cpp] view plain copy
String comdata = "";
Char terminator = ',';
Void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
While(Serial.read()》= 0){} //clear serialbuffer
}
Void loop() {
// read data from serial port
If(Serial.available()》0){
Delay(100);
Comdata =Serial.readStringUntil(terminator);
Serial.print("Serial.readStringUntil: â€);
Serial.println(comdata);
}
While(Serial.read()》= 0){}
}
Experimental result
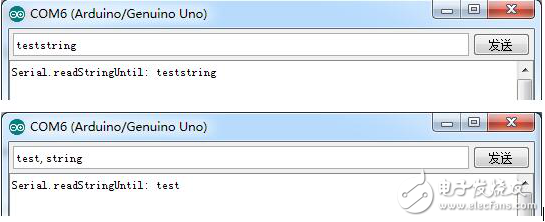
Read all characters from the serial port and store them in the string comdata until the character "," is encountered.
Serial.parseFloat();
Description
Read the first valid floating point data in the serial port buffer and the number will be skipped. The function ends when the first non-floating point is read.
grammar
Serial.parseFloat()
parameter
None
return
Returns the first valid floating point data in the serial buffer, and the number will be skipped.
Example
[cpp] view plain copy
Float comfloat;
Void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
While(Serial.read()》= 0){}//clear serialbuffer
}
Void loop() {
// read data from serial port
If(Serial.available()》0){
Delay(100);
Comfloat = Serial.parseFloat();
Serial.print("Serial.parseFloat:");
Serial.println(comfloat);
}
// clear serial buffer
While(Serial.read() 》= 0){}
}
Experimental result
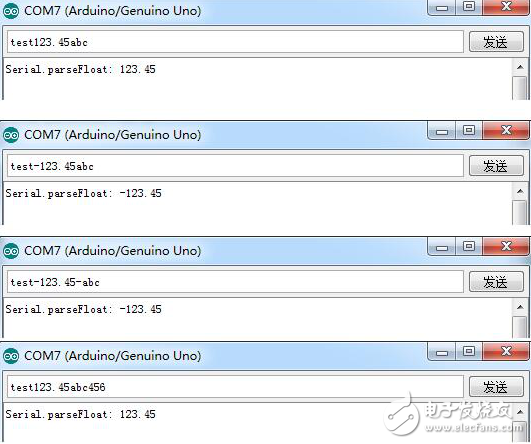
It can be seen from the experimental results that Serial.parseFloat() reads the first valid floating point number from the serial port buffer, the negative sign before the first significant digit will also be read, and the independent negative sign will be discarded.
Serial.parseInt()
Description
Reads the first valid integer (including negative numbers) from the serial receive stream.
note:
Non-numeric first or negative characters will be skipped
Analysis stops when the configurable timeout value does not read a valid character, or when a valid integer is not read
Returns 0 if it times out and does not read a valid integer
grammar
Serial.parseInt()
Serial.parseInt(charskipChar)
parameter
skipChar is used to skip the specified character in the search (this usage is unknown)
return
Returns the next valid integer value.
Example
[cpp] view plain copy
Int comInt;
Voidsetup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
While(Serial.read()》= 0){}//clear serialbuffer
}
Void loop() {
// read data from serial port
If(Serial.available()》0){
Delay(100);
comInt = Serial.parseInt();
Serial.print("Serial.parseInt:");
Serial.println(comInt);
}
// clear serial buffer
While(Serial.read() 》= 0){}
}
Experimental result
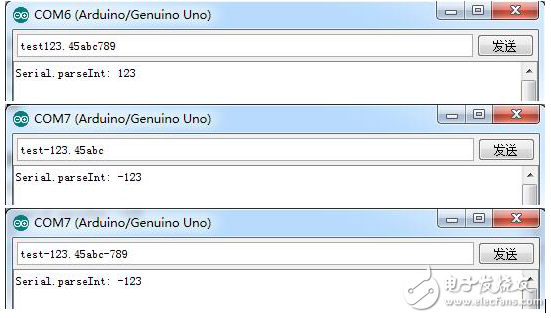
It can be seen from the experimental results that Serial.parseInt() reads the first valid integer from the serial port buffer, the negative sign before the first significant digit will also be read, and the independent negative sign will be discarded.
5. Serial port finds the specified string
Serial.find()
Description
Read data from the serial port buffer and look for the target string target (char type)
grammar
Char target[] = "target string";
Serial.find(target);
parameter
Target: target string (char type)
return
Find the target string to return true, otherwise false
Example
[cpp] view plain copy
Char target[] = "test";
Void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
While(Serial.read()》= 0){}//clear serialbuffer
}
Void loop() {
// read data from serial port
If(Serial.available()》0){
Delay(100);
If( Serial.find(target)){
Serial.print("find traget:");
Serial.println(target);
}
}
// clear serial buffer
While(Serial.read() 》= 0){}
}
Experimental result
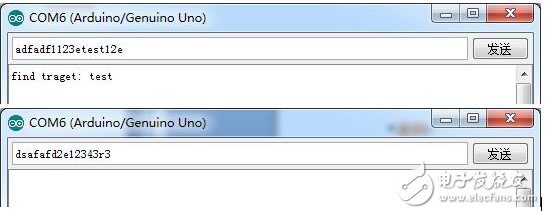
As long as there is test in the serial input character, the function returns true, and the target string "test" is printed. Otherwise, it returns false and no value is printed.
Serial.findUntil(target,terminal);
Description
Read data from the serial port buffer and look for the target string target (char array) until the given string terminal (char type) appears, find true, otherwise false.
grammar
Serial.findUntil(target,terminal);
parameter
Target : target string (char type)
Terminal : end search string (char type)
return
Returns true if the target character target is found before the termination character terminal is found, otherwise returns false.
Example
[cpp] view plain copy
Char target[] = "test";
Char terminal[] = "end";
Void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
While(Serial.read()》= 0){}//clear serialbuffer
}
Void loop() {
// read data from serial port
If(Serial.available()》0){
Delay(100);
If( Serial.findUntil(target,terminal)){
Serial.print("find traget:");
Serial.println(target);
}
}
// clear serial buffer
While(Serial.read() 》= 0){}
}
Experimental result
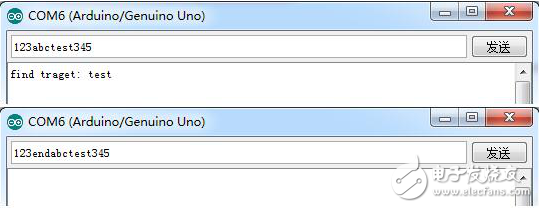
If the target character "test" is in the serial cache, it returns true, but if the termination string "end" is encountered first, the function terminates immediately, regardless of whether there is a target character "test" after the string.
6. Write data to the serial port
Serial.write();
Description
Serial output data function. Write binary data to the serial port.
grammar
Serial.write(val)
Serial.write(str)
Serial.write(buf, len)
parameter
Val: byte
Str: a string of bytes
Buf: byte array
Len: the length of buf
return
Byte length
Example
[cpp] view plain copy
Void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
}
Void loop(){
Serial.write(45); // send a byte with thevalue 45
Int bytesSent = Serial.write("hello"); //sendthe string "hello" and return the length of the string.
}
China Cable,High gain Cable.Factory Price Cable
RG58.LMR400.LMR200.Coaxial Cable.
Yetnorson Antenna Co., Ltd. , https://www.xhlantenna.com