Stupid and unclear - 3D printing, rapid prototyping and rapid manufacturing technology analysis Currently, 3D printing, 3D printer, 3D printing, rapid prototyping, rapid manufacturing, digital manufacturing, such as the same whirlwind, as if overnight Academic circles, political circles, the media, the financial industry, and the manufacturing industry have set off giants. However, there is still no article that can comprehensively and completely analyze these terms, so that people can truly understand and understand "what is 3D printing" and "what is rapid manufacturing."
Parsing one: concept
Rapid Prototyping (RP), born in the late 1980s, is a new technology based on material stacking and is considered to be a major achievement in the manufacturing field in the past 20 years. It combines mechanical engineering, CAD, reverse engineering technology, layered manufacturing technology, numerical control technology, material science, and laser technology. It can automatically, directly, quickly and accurately transform design ideas into functional prototypes or directly manufactured parts. This provides an efficient and low-cost means of achieving prototyping and verification of new design ideas. At present, the domestic media industry is accustomed to calling rapid prototyping technology "3D printing" or "3D printing", which is more vivid, but in fact, "3D printing" or "3D printing" is only a branch of rapid prototyping, which can only represent part of the rapid Molding.
Rapid Manufacturing (RM), which has narrow and broad sense, is a new manufacturing concept based on laser powder sintering rapid prototyping technology. It is actually a branch of RP rapid prototyping technology. It refers to electronic data. Fast, flexible and less costly manufacturing methods are performed directly and automatically. Rapid manufacturing Compared with general rapid prototyping technology, it can directly produce the final product, which can adapt to the individual product manufacturing from single product manufacturing to batch; in a broad sense, RM rapid manufacturing can include “quick mold†technology and CNC. CNC machining technology, so it can compete with RP rapid prototyping technology, each winning the field.
Internationally, "AddiTIve Manufacturing" (AM for short) is used to cover RP and RM technologies, and domestic translations are incremental manufacturing, additive manufacturing or additive manufacturing. In 2009, ASTM established the F42 committee, which defined AM as: "Process of joining mat-erials to make objects from 3d model data, usua-lly layer upon layer, as opposed to subtracTIve manufacturing methodologies." The material processing method is completely opposite. By adding materials and based on the 3D CAD model data, the manufacturing method of the 3D physical solid model which is completely consistent with the corresponding mathematical model is directly manufactured by the layer-by-layer manufacturing method.

Analysis 2: The molding principle and advantages and disadvantages of several mainstream rapid prototyping processes
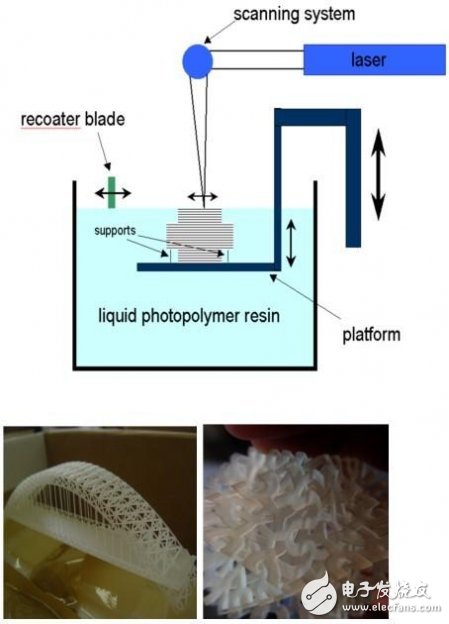
1. Laser light curing (SLA - Stereolithography)
The technology uses a photosensitive resin as a raw material, and the ultraviolet laser under computer control scans the liquid resin according to the contour of each layered section of the predetermined part, and then photopolymerization is generated by the thin layer of the resin in the scanning area, thereby forming a part. A thin section. When the layer is cured, move the workbench and apply a new layer of liquid resin to the surface of the previously cured resin for the next layer of scanning and curing. The newly cured layer is firmly bonded to the previous layer and is repeated until the entire part is prototyped. 3DSYSTEMS is the first company to introduce this technology. The technical feature is high precision and smoothness, but the materials are brittle, the running cost is too high, the post-processing is complicated, and the requirements for the operators are high. Suitable for verifying the assembly design process.
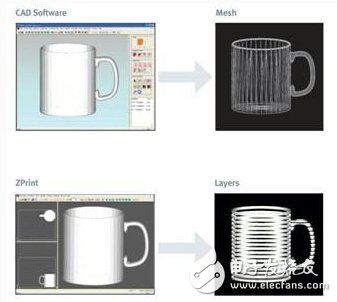
2. 3D printing (3DP - 3Dimension Printer)
Its biggest feature is miniaturization and easy operation, and it is mostly used in business, office, scientific research and personal studio environments. According to different printing methods, 3DP 3D printing technology can be divided into hot explosion type 3D printing (representative: Zprinter series of 3D Systems, USA - formerly ZCorporaTIon, which has been acquired by 3D Systems), piezoelectric 3D printing (Representative: ProJet series from 3D Systems, USA and 3D printing equipment from Objet, which was acquired by Stratasys recently), DLP projection 3D printing (representing: Ultravision, Perfactory series from Envisiontec, Germany).
The principle of the hot explosion type three-dimensional printing process is to send a certain amount of powder from the storage bucket, and then use the roller to lay the powder on the processing platform with a thin layer of raw material. The print head is sliced ​​according to the 3D computer model. The layer information is sprayed out of the station to stick the powder. After finishing one layer, the processing platform automatically drops a little, the storage bucket rises a little, the scraper pushes the powder from the raised storage bucket to the working platform and flattens the powder, so that the desired shape can be obtained by circulating. The technology is characterized by high speed (6 times that of other processes) and low cost (1/6 of other processes). The disadvantage is lower accuracy and surface finish. The Zprinter Series is the world's only 3D printing device capable of printing full color parts.

Piezoelectric three-dimensional printing, similar to traditional two-dimensional inkjet printing, can print ultra-high-resolution samples for rapid prototyping of small and delicate parts. Relative to SLA, equipment maintenance is simpler; surface quality is good, Z-axis precision is high.
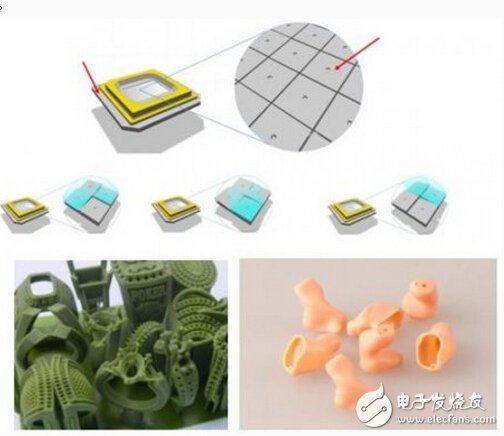
The forming principle of the DLP projection type three-dimensional printing process is to form the photosensitive resin by direct light forming technology (DLPR), the CAD data is layered and supported by computer software, and then the black and white Bitmap file is output. The Bitmap file for each layer is projected onto the workbench by the DLPR projector to cure it. Advantages of DLP Projection 3D Printing: Using the software that comes with the machine from the factory, you can automatically generate support structures and print out perfect 3D parts. Compared to other equipment in the rapid prototyping field, the unique voxelisaTIon patented technology guarantees the precision and surface finish of the molded product.

3. Fused Deposition Modeling
The FDM process, also known as extrusion molding, is about keeping the semi-flow molding material just above the melting point (usually controlled at about 10 °C above the melting point). The FDM nozzle is controlled by CAD layered data to make the semi-flow fuse material (the diameter of the wire is 1.5mm or more) extruded from the boring head, solidified to form a thin layer of contour shape, and a layer is layered to form the entire part. model. The BFB series and Rapman series products of 3DSYSTEMS Company of the United States all adopt FDM technology. The process features are directly made of engineering materials such as ABS and PC, which are suitable for different stages of design. The disadvantage is that the surface finish is poor.
Gas Generator,4 Cycle 16 Cylinders,4 Cycle 16 Cylinders Cummins Generators,4 Cycle 16 Cylinders Generators
XCMG E-Commerce Inc. , https://www.xcmg-generator.com