In 2015, a series of commercial activities led people's interest to the battery industry: Tesla launched the home Powerwall energy system, thanks to the production efficiency of its battery manufacturer Gigafactory, which is cheaper. Apple filed a patent for charging and power management of a solid-state battery device; LG Chem opened a large new energy vehicle power battery factory in Nanjing; Bosch acquired polymer solid-state battery company Seeo. There are also numerous investment, acquisition, cooperation and joint venture activities.
At the same time, new battery technologies are constantly emerging, and each technology is inseparable from such things as “double the performanceâ€, “just charge in a few minutesâ€, “cost is reduced by 70%â€, and so on. description of. This makes the public even more confused about what breakthroughs in technology. This article will discuss emerging technologies, new investment opportunities, and potential markets in the battery arena.
Looking for opportunities in different dimensions
Since Sony first introduced lithium-ion batteries to the market in the 1990s, it has become the most familiar and most commonly used battery technology in our daily lives. Lithium-ion battery related technologies have been relatively mature, and related facilities have been put in place. With the expansion of existing battery manufacturing giants such as Samsung SDI, LG Chem and Matsushita, the advantages of economies of scale have become more prominent. However, even with numerous advantages, advances in performance and cost reduction of lithium-ion batteries are still lagging behind other electronic devices.
Liquid electrolytes used in conventional lithium-ion batteries can pose serious safety hazards. On the other hand, with the development of wearable devices, printed electronics, Internet of Things (IoT), robots and electric vehicles, batteries with more features, better performance and lower prices are waiting to be introduced. These factors have prompted players in the battery circle to seek more investment opportunities.
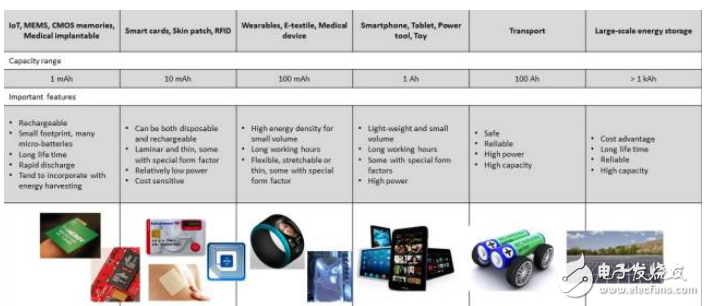
Therefore, the battery industry has many different dimensions to develop. The main interests of people fall in the following aspects:
Thin film battery (based on thickness)
ØMicro battery and large area battery (based on size)
Ø Flexible battery (based on physical characteristics)
Ø Shaped battery (according to the shape)
ØPrinted battery (according to manufacturing method)
Ø Solid state, lithium anode, silicon anode battery (based on technology)
Ø Energy Storage System (ESS) and Electric Vehicle (EV) (application based)
All of the above areas represent new opportunities. These areas may interact and overlap each other. For example, a more technically advanced battery can be used in ESS and EV, which gives the latter a higher safety factor and better performance. Thin film batteries can also be flexible, printed, or constructed of solid components, or even very mini.
Development roadmap for membrane flexible printing batteries. Image source: IDTechEx Research.
Further reduction in costs may not depend on technological advances
Advances in battery technology are subject to electrochemistry, making it difficult to achieve rapid and huge breakthroughs. In addition, practical batteries have many other factors to consider, such as energy density, specific power, lifetime, safety, and cost. Many news reports only emphasize one or some advances, but they ignore other aspects. Most existing commercial batteries rely on relatively mature, practically tested techniques, but sometimes they are not known, including thin-film solid-state batteries and printed batteries. Given the long and arduous process of battery development, future battery cost reductions will rely primarily on economies of scale rather than technological innovation.
Comcn Electronics Limited , https://www.comencnspeaker.com