Resistance is abbreviated as R, which is a basic property of conductors and is related to the size, material, and temperature of the conductor. Ohm's law states that the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance is I=U divided by R, that is, R=U divided by I. The basic unit of resistance is ohm, which is represented by the Greek letter "Ω". Usually "resistance" has two meanings, one is the physical quantity of "resistance" in physics, and the other refers to electronic components such as resistance.
The resistance value of a resistance element is generally related to temperature, material, length, and cross-sectional area. The physical quantity that measures the magnitude of resistance affected by temperature is the temperature coefficient, which is defined as the percentage of the resistance value that changes when the temperature increases by 1°C. The main physical characteristic of a resistor is to transform electrical energy into thermal energy. It can also be said that it is an energy-consuming element, and internal energy is generated when current passes through it. Resistors usually play a role in dividing voltage and current in a circuit. For signals, both AC and DC signals can pass through resistors.
The basic unit of resistance: Ohm, which can also be abbreviated directly as "Ohm". In order to facilitate the writing of larger values ​​of resistance, this unit is often abbreviated like current and voltage. There are kiloohms and megaohms. The conversion relationship between Europe is:
1000 ohms = 1 kiloohm
1000 kiloohms = 1 megaohm
1000 megohms = 1 gigohm

Definition: R=U to I
Definition formula: R=ÏL ratio S
Variation of Ohm's Law: R=U to I
Resistance series: R=R1+R2+R3+. .+Rn
Resistance in parallel: 1/R=1/R1+1/R2+1/R3+..+1/Rn
Formula related to electric power: R=U2/P; R=P/I2
Formula related to electric energy (electric heating): R=U2t/W; R=W/I2t (for electric heating, W is replaced by Q)
Decision formula: R=ÏL/S (Ï represents the resistivity of the resistor, which is determined by its own nature, L represents the length of the resistor, S represents the cross-sectional area of ​​the resistor)
Conversion of commonly used resistance units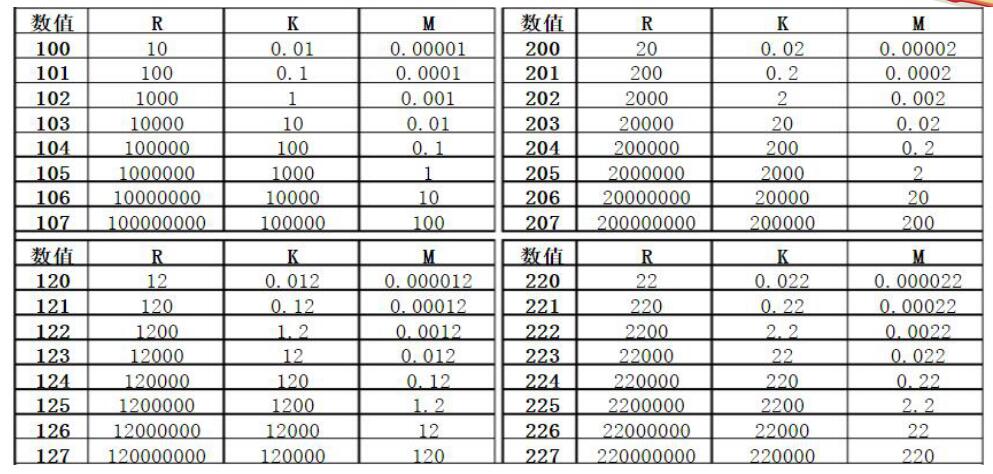
1. Unit: 1 ohm = 1 × 10 negative cubic kiloohm = 1 × 10 negative 6 power megaohm.
2. Specifications: Defined by the length and width of the component. There are 1005 (0402), 1608 (0603), 2012 (0805), 3216 (1206) and so on.
Representation method: 2R2=2.2 ohms, 1K5=1.5 kiloohms, M5=2.5 megaohms, 103J=10×10 cubes=10 kiloohms. 1002F=100×10 square=10 kiloohms (F and J refer to error, F refers to ±1% precision resistance, J is ±5% ordinary resistance, the performance of F is better than that of J).
The resistors are marked with numbers except for 1005, which represent the capacity of the resistor. The unit of the resistance value is usually: ohm. In addition, kiloohms and megaohms are also used. The relationship between them is as follows: 1 megaohm = 10 cubic kiloohms = 10 square ohms.
Portable Battery ,Portable Power Bank,Portable Battery Pack,Portable Power Pack
Zhejiang Casnovo Materials Co., Ltd. , https://www.casnovo-new-energy.com