This article is mainly about the related introduction of molded case circuit breakers and electronic molded case circuit breakers, and focuses on the differences between the two.
Molded Case Circuit BreakerMolded case circuit breakers can automatically cut off the current when the current exceeds the trip setting. Plastic case refers to the use of plastic insulators as the outer casing of the device to isolate the conductors and the grounded metal parts. Molded case circuit breakers usually contain thermal and magnetic trip units, while large models of molded case circuit breakers are equipped with solid state trip sensors. The trip unit is divided into: thermal magnetic trip and electronic trip. Commonly used, the rated current is as follows: 16 25 30 40 50 60 75 80 100 125 160 200 225 250 315 350 400 500 630 A.
Molded case circuit breakers are also called device-type circuit breakers. All parts are sealed in a plastic case. The auxiliary contacts, undervoltage releases and shunt releases are mostly modularized. Due to the very compact structure, the molded case circuit breaker cannot be overhauled. It mostly adopts manual operation, and large capacity can choose electric opening and closing. Due to the application of electronic over-current releases, molded case circuit breakers can also be divided into two types: A and B. Type B has good three-stage protection characteristics. However, due to price factors, thermal magnetic releases are used. Class A products have a higher market share. Molded case circuit breaker is the contact, arc extinguishing chamber, trip unit and operating mechanism are all installed in a plastic shell, generally do not consider maintenance, suitable for branch circuit protection switch, overcurrent release has thermomagnetic There are two types of thermal-magnetic molded case circuit breakers. Generally, the thermal-magnetic molded case circuit breaker is a non-selective circuit breaker. There are only two protection methods: overload long delay and short circuit instantaneous protection. Electronic molded case circuit breakers have overload long delay and short short circuit protection. Four protection functions: time delay, instantaneous short circuit and ground fault. Some of the newly launched products of electronic molded case circuit breakers also have a regional selective interlocking function. Most molded case circuit breakers are manually operated, and some have motor operating mechanisms.
working principle
The main contact of the low-voltage circuit breaker is manually operated or electrically closed. After the main contact is closed, the free trip mechanism locks the main contact in the closing position. The coil of the overcurrent release and the thermal element of the thermal release are connected in series with the main circuit, and the coil of the undervoltage release is connected in parallel with the power supply. When the circuit is short-circuited or severely overloaded, the armature of the overcurrent release pulls in, causing the free tripping mechanism to operate, and the main contact disconnects the main circuit. When the circuit is overloaded, the thermal element of the thermal trip unit generates heat to bend the bimetallic strip, pushing the free trip mechanism to act, and the main contact disconnects the main circuit. When the circuit is under-voltage, the armature of the under-voltage release is released, which also causes the free trip mechanism to act, and the main contact disconnects the main circuit. When the shunt trip button is pressed, the armature of the shunt trip unit pulls in, causing the free trip mechanism to act, and the main contact disconnects the main circuit.
Working conditions
◠Ambient air temperature ○ Upper limit of ambient air temperature +40℃; ○ Lower limit of ambient air temperature -5℃; ○ The average value of ambient air temperature for 24 hours does not exceed +35℃. ◠Altitude: The altitude of the installation site does not exceed 2000m. ◠Atmospheric conditions: the relative humidity of the atmosphere does not exceed 50% when the ambient air temperature is +40℃; it can have a higher relative humidity at a lower temperature; the average maximum relative humidity of the wettest month is 90%, and at the same time the month The monthly average minimum temperature of +25℃, and taking into account the condensation on the surface of the product due to temperature changes. ◠Pollution degree: The pollution degree is level 3.
The main parameters
â‘´Rated voltage The rated voltage on the nameplate of the circuit breaker refers to the rated voltage of the main contact of the circuit breaker, which is the voltage value that guarantees the long-term normal operation of the contactor of the contactor.
(2) Rated current The rated current on the nameplate of the contactor refers to the rated current of the main contact of the circuit breaker, and is the current value that guarantees the long-term normal operation of the contactor of the contactor.
⑶ Tripping current The tripping current is the current setting value that causes the overcurrent release to operate. When the circuit is short-circuited or the load is seriously overloaded, and the load current is greater than the tripping current, the main contact of the circuit breaker is opened.
â‘·Overload protection current, time curve The overload protection current and time curve are inverse time characteristic curves. The larger the overload current, the shorter the time for the thermal release to act.
⑸ Rated voltage of the undervoltage release coil The rated voltage of the undervoltage release coil must be equal to the rated voltage of the line.
⑹ The rated voltage of the shunt release coil. The rated voltage of the shunt release coil must be equal to the control power supply voltage.
⑺ Rated ultimate short-circuit breaking capacity Icu The breaking capacity index of circuit breakers has two types: rated ultimate short-circuit breaking capacity Icu and rated operating short-circuit breaking capacity Ics. The rated ultimate short-circuit breaking capacity Icu is the limit parameter of the breaking capacity of the circuit breaker. After several short-circuit faults are broken, the breaking capacity of the circuit breaker will decrease. The rated operating short-circuit breaking capacity Ics is a breaking index of the circuit breaker, that is, the normal operation of the circuit breaker can be guaranteed after several short-circuit faults have been broken. For molded case circuit breakers, as long as the Ics is greater than 25% Icu, it is considered qualified. At present, the Ics of circuit breakers on the market are mostly between (50%-75%) Icu.
â‘» Current-limiting and breaking capacity Current-limiting and breaking capacity refers to the ability to limit the fault current when the circuit breaker trips when a short circuit occurs. When the circuit is short-circuited, the contacts of the circuit breaker open rapidly and an arc is generated, which is equivalent to inserting a rapidly increasing arc resistance in the line, which limits the increase of fault current and reduces the electromagnetic, electrical and thermal effects of the short-circuit current. Adverse effects on circuit breakers and electrical equipment, prolong the service life of circuit breakers. The shorter the breaker opening time, the better the current limiting effect, and the closer Ics is to Icu.
⑼ Tripping characteristics of miniature circuit breakers The tripping characteristics of circuit breakers are divided into A, B, C, D, K, etc., and their respective meanings are as follows: Type A tripping characteristics: Tripping current is (2~3) In, Suitable for protecting semiconductor electronic circuits, measuring circuits with low-power power transformers, or systems with long circuits and low short-circuit current; Type B tripping characteristics: tripping current is (3 ~ 5) In, suitable for household power distribution systems, Protection of household appliances and personal safety; C-type tripping characteristics: tripping current is (5~10) In, suitable for protecting power distribution lines and lighting circuits and motor circuits with higher on-current; D-type tripping Features: The tripping current is (10-20) In, which is suitable for protecting equipment with high inrush current, such as transformers, solenoid valves, etc.; K-type tripping characteristics: 1.2 times the thermal tripping current and 8-14 times The magnetic tripping action range is suitable for protecting motor circuit equipment, and has a high resistance to impact current.
Electronic Molded Case Circuit BreakerThe electronic molded case circuit breaker constructed with the microprocessor-based measurement and control system is far superior to the traditional thermal magnetic circuit breaker in terms of selectivity, quick action, reliability and safety and other key characteristics, and is more adaptable The development trend of increasingly complex power distribution networks and increasingly diversified electrical equipment has laid a good technical foundation for the realization of power distribution management automation
CM1E electronic molded case circuit breaker is used for infrequent conversion and motor protection in circuits with AC 50HzHz, rated working voltage up to 690V, and rated current up to 1250A. The circuit breaker has overload long delay inverse time limit, short circuit short delay inverse time limit, short circuit short delay time limit, short circuit instantaneous and undervoltage protection functions, which can protect the circuit and power equipment from damage, and can provide low temperature to -40℃ breaker. Circuit breakers are classified into M type and H type according to their rated ultimate short-circuit breaking capacity. The circuit breaker has the characteristics of small size, high breaking, short arcing, and anti-vibration. The circuit breaker can be installed vertically or horizontally.
working principle
The electronic molded case circuit breaker adopts an intelligent controller to replace the traditional thermal magnetic trip unit. The main function of the intelligent controller in the power supply and distribution system is to detect and protect the overload, short circuit and other faults in the line. The principle block diagram is shown in Figure 1. The current transformer is used to detect the current signal of the main circuit, and the effective calculation and logic signal control are completed by the intelligent controller; when the intelligent controller detects the fault current, it will command within the specified time The flux converter forces the circuit breaker to trip. The intelligent controller includes a rectifier circuit, a signal conditioning circuit, a power supply circuit, a MicroControlUnit (MCU), a trip circuit, MCU required circuits, a man-machine interface, and a regional selective interlocking control circuit.
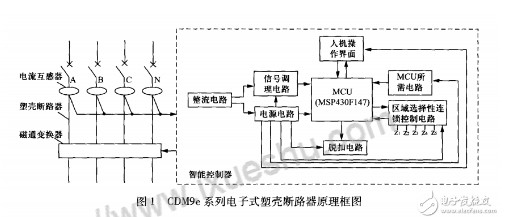
Conditions of Use
1. The ambient air temperature is -5℃~+40℃.
2. The altitude of the installation site does not exceed 2000mm.
3. The relative humidity of the air at the installation site does not exceed 50% when the maximum temperature is +40℃, and it can have a higher relative humidity at a lower temperature.
4. The pollution level is level 3.
5. The installation category of the main circuit is â…¢, and the installation category of the other auxiliary circuits and control circuits is â…¡.
6. It can withstand the influence of humid air, salt spray, oil mist and mold.
7. It should be installed in a place where there is no explosion hazard, no conductive dust, no sufficient corrosion of metals and damage to insulation.
8. It should be installed in a place where there is no rain and snow.
The difference between electronic molded case circuit breaker and ordinary molded case circuit breakerMCCB has only two types: electromagnetic and electronic. Electromagnetic type means that the overload protection module is composed of thermomagnetic components, that is, bimetallic sheet + magnetic coil; while electronic type means that the overload protection module is composed of CT/PT + electronic components.
Both of these protection modules can perform long-delay, short-delay, and instantaneous protection, but the action current and time accuracy are different. Of course, the price is also far away. For the budget, choose the electronic type, and vice versa, the electromagnetic type.
The difference between molded case circuit breaker and electronic molded case circuit breaker
Molded case circuit breaker is the contact, arc extinguishing chamber, trip unit and operating mechanism are all installed in a plastic shell, generally do not consider maintenance, suitable for branch circuit protection switch, overcurrent release has thermomagnetic There are two types of thermal-magnetic molded case circuit breakers. Generally, the thermal-magnetic molded case circuit breaker is a non-selective circuit breaker. There are only two protection methods: overload long delay and short circuit instantaneous protection. Electronic molded case circuit breakers have overload long delay and short short circuit protection. Four protection functions: time delay, instantaneous short circuit and ground fault. Some of the newly launched products of electronic molded case circuit breakers also have a regional selective interlocking function. Most molded case circuit breakers are manually operated, and some have motor operating mechanisms.
Molded case circuit breaker thermo-electromagnetic type, most of the previous circuit breakers have this structure, which uses the thermal effect of electricity and the magnetic effect of electricity. The thermal effect is implemented by the bimetal structure. When the switching current is large, the bimetal is bent Deformation, push the tripping device of the switch after the deformation to a certain extent, the switch trips, adjust the thermal overload current of the switch through the mechanical adjustment screw, the adjustment accuracy is not high, it is an inverse time action, that is, the greater the current, the shorter the action time , Some large switches such as electric circuit breakers.
The thermal overload current does not directly adopt the bimetal structure, but uses a current transformer to convert the primary current into a secondary current. When the thermal relay is connected, the normally open or normally closed contact of the thermal relay is used to control the trip coil. Turning off the switch, the instantaneous high-current trip is to use the magnetic effect. There is a structure like an electromagnetic coil at the lower end of the switch. When there is a large current or a short-circuit current (which is much larger than the overload current of the switch 0, the electromagnetic coil’s suction force will increase directly. The switch trip device is driven, and the instantaneous trip current of the switch is adjusted through the mechanical adjustment screw.
The thermal electromagnetic structure does not require an external power supply and has strong anti-interference. It is not necessary to use a trip coil.
The electronic type is to check the switch current through the current transformer loop, the current value is used to control the output, and the output controls the trip coil to make the switch trip. The advantages are high precision and easy adjustment. You can set the value directly or use a potentiometer to adjust.
The disadvantage is that it needs to use a trip coil and a power supply. It is more difficult to deal with problems in the electronic circuit, and the anti-interference ability is poor.
ConclusionThis concludes the introduction of the difference between molded case circuit breakers and electronic molded case circuit breakers. I hope this article will give you a more comprehensive understanding of the difference between molded case circuit breakers and electronic molded case circuit breakers.
Car Radio Antenna.car satellite TV Antenna.High gain car radio antenna
car radio Fm/AM antenna,car satellite tv antenna,High gain car radio antenna
Yetnorson Antenna Co., Ltd. , https://www.xhlantenna.com