Lu Liang Jiang Xiaomei Zhao Zhidan China Institute of Metrology
1. Introduction For the past 30 years, the technology of LED light-emitting diodes has experienced a rapid development process. LED has been widely used due to its inherent high efficiency, long life, low loss, vibration resistance, fast response, etc., such as indicator lights, display screens, traffic lights, etc., is currently being explored for its application in the field of lighting.
Since China has not established LED photometric standards, it has seriously affected the improvement of LED product quality and the unification of quantity, affecting the exchange and promotion of international trade and international LED technology. Therefore, although the quality of LED products in China in recent years And the variety has improved, but the gap is more obvious than the advanced countries.
In this situation, we proceeded to conduct a detailed study on the measurement of LED optical parameters, and carried out the establishment of LED national photometric standards.
2, LED light parameters introduction
The important aspects of the optical parameters of LEDs are: luminous flux, luminous efficiency, luminous intensity, light intensity distribution, and wavelength.
2.1 Luminous efficiency and luminous flux Luminous efficiency is the ratio of luminous flux to electrical power. Luminous efficiency characterizes the energy-saving characteristics of a light source, which is an important indicator of the performance of modern light sources.
2.2 Luminous intensity and light intensity distribution LED luminous intensity is to characterize its intensity in a certain direction. Since the LEDs have different light intensity in different spatial angles, we have studied the light intensity distribution characteristics of LEDs. . This parameter is of great practical significance and directly affects the minimum viewing angle of the LED display device. For example, the LED large-scale color display of the stadium, if the LED single tube distribution range is narrow, the audience facing the display at a large angle will see the distorted image. And traffic signs also require a large range of people to identify.
2.3 Wavelength For the spectral characteristics of LEDs, we mainly look at whether its monochromaticity is excellent, and it should be noted whether the main colors such as red, yellow, blue, green and white LEDs are pure. Because in many occasions, such as traffic lights, the color requirements are more stringent, but it is observed that some of China's LED signal lights are green and blue, and red is dark red. From this phenomenon, we have studied the spectral characteristics of LEDs. It is very necessary and very meaningful.
3. Principle of LED photometric measurement 3.1 Measurement method of light intensity The light intensity standard lamp, LED and silicon photodiode equipped with V(λ) filter are installed and debugged on the optical bench, especially the filament is strictly adjusted. Position, LED lighting position and receiving surface position.
First calibrate the silicon photodiode with a light standard lamp, C=E/S
Where Es=IS/(d 2 s)
Ds is the distance between the standard lamp and the receiver, Is is the light intensity of the standard lamp, and Rs is the response of the standard lamp.
Es=C·R t where E t is the illuminance of the LED under test, R t is the response of the LED under test, then the light intensity I t of the LED is: I t =E t ·d 2 t where d t is the LED The distance from the receiving surface.
For LEDs, the light-emitting surface is in the shape of a dome, and the light distribution is very special. Therefore, at different measurement distances, the light intensity value will change, and the deviation distance square inverse law will be fixed even if the measurement distance is fixed. The light intensity value will also vary depending on the receiving area. Therefore, in order to improve the measurement accuracy, it is preferable to fix the measurement distance and the acceptance area size relatively. For example, the measurement distance is 316 mm as recommended by the CIE and the receiver area is fixed at 10 x 10 mm. At the same measuring distance, the LED angle varies with its light intensity, so in order to obtain the optimum value, it is better to read the maximum reading R t .
3.2 Measurement of luminous flux The luminous flux measurement is carried out on the turntable of the variable angle photometer. The LED is turned on the turntable. The turntable is rotated by ±90 degrees around the vertical axis on its horizontal plane. The LED is around the vertical plane for metering. The shaft rotates 360 degrees. The control of the corners on the horizontal and vertical planes is achieved by a stepper motor. The turntable moves freely on the guide rails. When measuring standard lights, the turntable should leave the guide rails.
When measuring, the large turntable rotates on the horizontal plane around the vertical axis with a step angle of 0.9°, a positive direction of 90°, and a reverse direction of 90°. The LED itself is also rotating. At each horizontal angle, the signal is collected every 18° on the vertical plane. After 360°, a total of 20 data are collected, and the total luminous flux is calculated by the following formula.
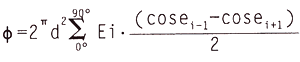
If the market is rotated from 0° to 90°, the small disk can be rotated from 0° to 360°. However, when the large disk rotates from 0° to 90°, there is a possibility that the LED is unevenly mounted (asymmetric) and causes an error. Therefore, the best solution is to turn the large disk to -90° to 0° to 90°, and the small disk still turns to 0°. 360°, the illuminance values ​​at the angles where the absolute values ​​of the large plates are equal to each other in the range of 0° to 90° and −90° to 0° are averaged as values ​​within 0° to 90°.
The second method of measuring the total luminous flux of an LED is the integral method. The advantage of this method is that it is simple and easy, but the measurement accuracy is not high. The total luminous flux calculation method of the LED is as follows. First, calculate the luminous flux Φ s , Φ s =I s ·A/ from the standard lamp (light intensity value I s ) entering the integrating sphere from the incident window of the integrating sphere (incident window area A). I 2 reads out the photocurrent signal i s on the receiver, then places the LED on the window and reads out the corresponding receiver photocurrent signal it, then the total luminous flux Φ of the LED is:
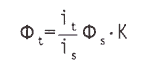
Where K is the color correction factor.
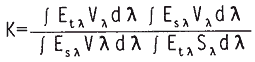
3.3 LED spectral power distribution measurement method:
The spectral power distribution measurement of the LED is designed to grasp the spectral characteristics and chromaticity of the LED, and is to correct the measured metric of the LED.
When measuring the spectral power distribution of LEDs, the following points should be noted. One is because the spectral intensity of the standard lamp is much stronger than that of the LED when compared with the standard spectral irradiance. In order to avoid this problem, it is better to be in front of the standard lamp. Add a neutral filter to make it spectrally close to the LED.
The spectral width of the LED is very narrow. In order to accurately depict the spectral distribution profile of the LED, it is preferable to measure with a narrow-band wavelength-width monochromator with a wavelength interval of 1 nm.
The spectral power distribution Et of the LED is calculated as follows.
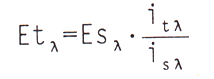
Where i is the response of the standard lamp at wavelength i; E is the spectral power distribution of the standard lamp; i is the response of the LED at wavelength λ.
The color coordinate calculation formula of the LED is:
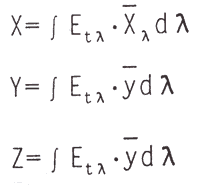
The color coordinates are:
x=X/(X+Y+Z)
y=X/(X+Y+Z)
The main wavelength and color purity of the LED can also be calculated.
4, the conclusion
At present, the national photometric standard device of LED has established and calibrated a considerable number of standard LED tubes. In the process, we have accumulated a lot of experience. After that, we will carry out the measurement and transfer of the measurement departments at all levels and the comprehensive LED production units. . This will promote the improvement of the quality level of LED in China, and will also provide protection for one aspect of research and development in the national high-tech field.
Component Mounting And Soldering.The final step is to mount and solder the components. Both THT and SMT components are placed on the PCB by machines. THT components are most often soldered in an automated process called 'Wave Soldering'. This enables all components to be soldered simultaneously. Their legs are first cut near the board and slightly bent over to keep the component in place. The PCB is then moved over a wave of liquid flux, such that the bottom side strikes the flux. This removes any oxide from the metal surfaces. After heating the PCB it is similarly moved over a wave of melted solder. The solder attaches to the solder pads and component legs, and the soldering is complete.
Component Mounting
Component Mounting,Custom Component Mounting,Metal Component Mounting,Mount Bracket Component
Orilind Limited Company , http://www.orilind.com