1, the background
First, as users demand higher and higher access to broadband access, existing broadband access methods, such as ADSL and LAN access, have short transmission distances, limited access bandwidth, low security, and no QoS. Very good guarantees and other issues have become increasingly unable to meet the needs of users. Second, optical access technologies are rapidly evolving, from active optical access technologies (PDH, SDH, MSTP, point-to-point Ethernet systems) to PON passive optical access technologies (APON, BPON, GPON, EPON, GEPON) . Finally, due to the cost of the fiber itself, the cost of the optical transceiver module, the OLT and the ONU, and the cost of supporting the existing fiber-to-the-home are declining, so that the equipment cost and line cost of the fiber-to-the-home are much larger than before. decline. Therefore, the fiber-to-the-home access method has gradually matured, and it has gradually become a hot spot in the domestic and international communication industry. In the near future, it will become an important means of user access. However, among the many fiber access technologies currently available, which fiber access technology is more suitable for the large-scale development of FTTH?
2. Active fiber access technology
2.1 PDH
PDH technology is widely used in the optical access field for its maturity. Its security and high QoS guarantee performance make it an important fiber access technology for telecom operators for a period of time. However, traditional PDH technology inevitably has certain limitations in access applications, mainly reflected in:
(1) Lack of unified network management;
(2) Lack of networking capabilities;
(3) Poor protection of the business;
(4) Lack of effective means of carrying on the rapidly growing IP data services;
(5) lack of flexibility in capacity expansion and upgrade;
(6) The interface is single, the devices are stacked, the external cable connection is more, and the number of fault points is increased, which brings difficulties to maintenance.
PDH optical access technology is mainly applied to enterprise users of point-to-point small-capacity private lines.
2.2 SDH
Compared with PDH, SDH, which is widely used in fiber access of enterprises and enterprises, has the following obvious advantages:
(1) Uniform bit rate and unified interface standard to facilitate interconnection between devices;
(2) Network management capabilities have been greatly enhanced;
(3) It has a self-healing protection function.
The main disadvantage of SDH is that it is designed to transmit TDM information. This technology lacks the functions required to process information other than traditional voice information based on TDM technology, and is not suitable for transmitting ATM and Ethernet services other than TDM.
SDH optical access technology is mainly used for point-to-point high-capacity private line enterprise users, inter-office or tandem-point (POP) communication.
2.3 MSTP
Based on SDH and simultaneous access, processing, and transmission of services such as TDM, ATM, and Ethernet, providing MSTP for unified network management has the following advantages:
(1) Provide a variety of physical interfaces to meet the fast access of new services. While ensuring compatibility with traditional TDM services, it can provide flexible access for multiple services. Typical services are: IP, ATM, SDH, FR.
(2) Since it is based on the existing SDH transmission network, it can be well compatible with existing technologies to ensure existing investments.
(3) MSTP uses VC virtual concatenation technology to effectively utilize bandwidth and achieve bandwidth management of smaller particles.
(4) MSTP adopts LCAS technology to ensure that the number of virtual concatenations is dynamically adjusted without interrupting the data flow.
(5) MSTP technology supports networking modes such as mesh, tree, star, and multi-ring cutting. This can improve the scalability of the network and facilitate flexible and efficient configuration of the system environment.
(6) High reliability and automatic protection recovery function of transmission. MSTP inherits the protection features of SDH, and the automatic protection recovery is less than 50ms, ensuring the user's satisfaction with the service.
The main disadvantages of MSTP are:
(1) Low bandwidth utilization;
(2) The maximum available bandwidth is limited;
(3) Mainly implement the two-layer function, and the relatively simple three-layer function;
(4) Insufficient flexibility in providing business capabilities.
(5) The fiber is occupied more
MSTP applications are mainly targeted at inter-office or tandem point-to-point communications as well as point-to-point communications for large enterprise users.
2.4 Point-to-Point Ethernet System
The point-to-point Ethernet system is the most direct Ethernet fiber access technology. Each user is directly connected to a user optical interface of the central office Ethernet switch through a pair of optical fibers. In the point-to-point Ethernet system mode, the extended Ethernet OAM protocol enables remote management of the customer premises equipment through the central office switch, thereby providing a carrier-class operational and manageable Ethernet access mode.
2.4.1 Advantages
(1) The access bandwidth is high and the network upgrade is convenient;
(2) The network hierarchy is simple, and the access network and the user Ethernet are seamlessly connected;
(3) The Ethernet switch is placed in the building, the cell or the central office room, and the central office and the user end are directly connected by optical fibers, and the entire access network has a simple structure;
(4) High business opening rate and fast investment recovery;
(5) The central office switch can remotely manage the user equipment, and the line detection and fault location can be easily performed at the central office, thereby reducing the maintenance difficulty.
2.4.2 Disadvantages
(1) Re-laying the fiber optic line;
(2) Each user occupies one/pair of optical fibers, and the number of optical fibers is large, which is difficult to construct;
(3) Because the inherent mechanism of Ethernet technology does not provide end-to-end packet delay, packet loss rate and bandwidth control, it is difficult to guarantee the quality of service of real-time services, and it is difficult to provide TDM services;
(4) High maintenance costs;
(5) Lack of security mechanism guarantee;
2.4.3 Application
When users are very dense, the space requirements and costs of the equipment room also increase rapidly, so it is not suitable for high-density user areas, and is more suitable for distributed user access.
3. Passive fiber access technology
Passive Optical Network (PON) means that the Optical Distribution Network (ODN) between the OLT (Optical Line Terminal) and the ONU (Optical Network Unit) does not have any active electronic equipment. Its typical topology is a point-to-multipoint star structure (as shown in Figure 1). No need for node equipment at the optical branch point, only a simple passive optical splitter needs to be installed, thus saving optical cable resources, sharing bandwidth resources, saving investment in the equipment room, high security, low comprehensive network construction cost, and low maintenance cost. High reliability.
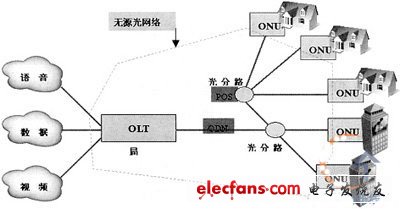
Figure 1 Passive Optical Network (PON) Topology
Disadvantages of PON fiber access technology:
(1) The initial investment cost is too high;
(2) Its topology makes the user not have a protection function or the protection cost is too high.
The application of PON fiber access technology is mainly suitable for distributed small enterprises and residential users, especially those small-area dense user areas where user areas are relatively dispersed and users in each area are relatively concentrated.
At present, PON-based fiber access technologies include APON, BPON, GPON, EPON, and GEPON. Since APON and BPON are based on ATM, ATM is not a development direction, and its rate is limited, and the equipment is complex, which cannot meet the high bandwidth of users. Low cost requirements, therefore, APON and BPON are not the development direction. This paper mainly introduces EPON/GEPON and GPON fiber access technologies.
Pre-Terminated Mini Cable,Pre Terminated Double Sheath Cable,Pre-Terminated Cable For 5G Network,Pre Terminated Cable For Telecommunication
ShenZhen JunJin Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.jjtcl.com