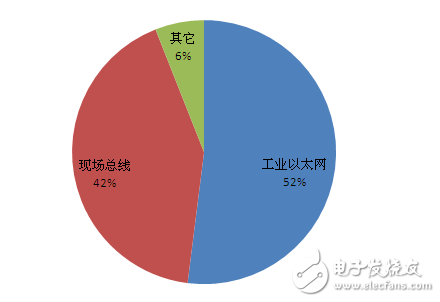
The data shows that the number of industrial Ethernet node installations increased from 46% in 2016 to 52% in 2017, while fieldbus dropped from 48% to 42%. Among them, EtherNet/IP is currently the most widely installed industrial Ethernet, with a market share of 15%, followed by PROFINET and PROFIBUS accounting for 12%, while wireless technology maintains a market share of 6%.
With the rapid evolution of the Industry 4.0 model, device interconnection has become increasingly important. Numerous machine connection requirements at the production site have driven the industrial Ethernet market to rise. According to the latest results of the Swedish Industrial Network's HMS annual survey of the industrial IoT market, Ethernet installation nodes for factory automation in 2017 exceeded traditional fieldbus for the first time.
The data shows that the number of industrial Ethernet node installations increased from 46% in 2016 to 52% in 2017, while fieldbus dropped from 48% to 42%. Among them, EtherNet/IP is currently the most widely installed industrial Ethernet, with a market share of 15%, followed by PROFINET and PROFIBUS accounting for 12%, while wireless technology maintains a market share of 6%.
The intelligent transformation of manufacturing requires high-performance networks to support, and the integration of IoT solutions and plant equipment is driving the use of industrial Ethernet. Industrial Ethernet has been in a transitional phase for a long time, and industrial Ethernet has replaced fieldbus in terms of the number of installed nodes.
According to HMS report, although the field bus lost to industrial Ethernet in the market, the number of fieldbus installations increased in 2017, and its growth rate increased from 4% in 2016 to 6%. It can be seen that the industrial network market is in the process. The stage of rapid development. However, network providers believe that the number of fieldbus installations will decline steadily in the next few years.
In 2017, the number of industrial wireless communication installation nodes increased by 32% compared with 2016. Although wireless technology is expanding, the market share is relatively small, and the market share is maintained at 6%. Among them, WLAN is currently the most popular wireless technology, followed by Bluetooth. Wireless communication technology can reduce cabling and facilitate device connectivity and control, and is increasingly being used by machine builders and system integrators to implement innovative solutions, including solutions such as monitoring via a tablet or smartphone.

The analysis found that Profinet and EtherNet/IP are the main network protocols in Europe and the Middle East. Profibus is widely used, and its networks including EtherCat, Modbus TCP and Ethernet Powerlink are also popular. The US market is more obvious to EtherNet/. IP development; in the Asian market, Profinet, EtherNet/IP, Profibus, EtherCat, Modbus and CC-Link are widely used.
Why do manufacturers favor industrial Ethernet?Industrial Ethernet is actually the application of Ethernet in the industry. Due to the harsh environment in the field, equipment connections often require stronger connectors and cables, and one of the most important is certainty. In order to achieve better certainty, Industrial Ethernet uses a proprietary protocol. Currently, the more popular industrial Ethernet protocols are PROFINET, EtherNet/IP, EtherCAT and POWERLINK.
Industrial Ethernet typically has data rates ranging from 10 Mbit/s to 1 Gb/s, with 100 Mbit/s being the most popular speed in industrial Ethernet applications. Industrial Ethernet requires some additional considerations, not Ethernet systems used in the office. For example, users need to monitor the temperature, vibration, noise, and other parameters of the production equipment in the factory in real time through the network.
Industrial Ethernet protocols such as PROFINET and EtherCAT have been modified from traditional Ethernet standards to ensure that the correct transmission and reception of manufacturing equipment data, as well as the ability to send and receive commands on time when the system needs to perform certain operations. For example, in the automated filling production process, the filling data needs to be sent over the network to ensure that the bottle filling is as expected, and an automated report is generated in real time. When the bottle is full, a command to stop filling is issued on the network.
The real-time and certainty of industrial Ethernet networks is important if data loss or delay between devices in an industrial environment can cause disasters. The industrial environment must ensure that the state of the automated production process is perceived in real time and that the plant process requirements can be completed in harsh environments.
Edge Automation and Opportunity for IIoTWith the advent of deterministic industrial Ethernet protocols and zero-fault redundancy protocols, some industry vendors have proposed to develop sensors based on Industrial Ethernet EtherNet/IP connections, but others have indicated that there is no need to use Ethernet-enabled sensors because of IO. -Link, HART or WirelessHART can be connected to the sensor and enter the Industrial Ethernet via the conversion device. Some process industry suppliers have developed potential new standards for connecting sensors to Industrial Ethernet via fieldbus.

In the past, many people in the automation industry insisted that industrial Ethernet will not extend to sensors, instrumentation and testing equipment, but today the industry 4.0 era has arrived, and the Internet of Things solution has further advanced the intelligent development of edge devices. Industrial Ethernet terminal equipment, including sensors and I/O drivers, will play a key role in future connectivity business strategies. In order to extend the analytical capabilities of the device, Industrial Ethernet must be extended to the last device in the automation chain: sensors and I/O.
Equipment managers want to make more use of plant-level information for business decisions, so they turn their attention to smart products like sensors and I/O. The ability to import data into cloud applications further facilitates the need for large data throughput and Ethernet-enabled end devices that exceed the capabilities of most dedicated legacy automation networks.
Industrial Ethernet equipment meets the needs of IIoT and Industry 4.0, such as reducing machine downtime and increasing production flexibility, and Industrial Ethernet and wireless will be the main drivers of these goals.
Heat Shrinkable Tube,Shrink Tube,Heat Shrink Sleeve,Clear Heat Shrink Tubing
Shenzhen Huiyunhai Tech.Co., Ltd. , https://www.cablesleevefactory.com